Wrist Surgery

Wrist Surgery
Treatment for wrist injuries depends on the type and severity of the injury. Mild injuries may be treated with rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medications. More severe injuries may require immobilization with a cast or brace, physical therapy, or surgery. It is important to seek medical attention for any wrist injury to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Our Popular Services
Hip Replacement Surgery
Knee Replacement Surgery
Spine Surgery
Shoulder Joint Replacement Surgery
Arthroscopic Surgery
Elbow Joint Replacement Surgery
Fracture Treatment
Sports Injuries
Some common wrist injuries
Wrist injuries are common and can occur due to a variety of reasons, including sports activities, falls, and accidents
Sprains
Fractures
Tendonitis
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Treatment For Wrist Injuries
Arthroscopy: Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which a small camera and instruments are inserted into the wrist joint through small incisions. This procedure is often used to diagnose and treat conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, wrist fractures, and ligament injuries.
Fracture repair: Wrist fractures may require surgery to realign and stabilize the broken bones. This may involve the use of pins, screws, or plates to hold the bones in place as they heal.
Joint replacement: In cases of severe arthritis or other joint damage, a wrist joint replacement surgery may be necessary to replace the damaged joint with an artificial joint.
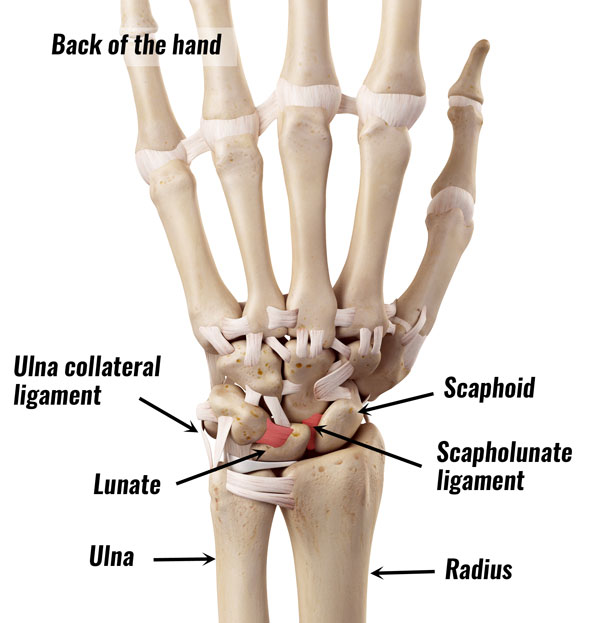
There are several steps you can take to help prevent wrist injuries
Warm-up and stretch before physical activity: Take the time to properly warm up and stretch your wrists and hands before engaging in any physical activity that involves using your wrists, such as playing sports or lifting weights.
Use proper technique: When performing any activity that involves the wrists, use proper technique to help reduce the risk of injury. For example, when typing or using a computer mouse, make sure your wrists are in a neutral position and avoid excessive bending or twisting.
Take frequent breaks: If you perform repetitive tasks that involve your wrists, such as typing or using a computer mouse, take frequent breaks to stretch and rest your wrists.
Wear protective gear: If you engage in sports or activities that involve a risk of wrist injury, wear appropriate protective gear, such as wrist guards or gloves.
Maintain good posture: Maintaining good posture can help reduce the strain on your wrists and hands.
Strengthen your wrists: Strengthening exercises for your wrists and hands can help improve their flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
Be mindful of your wrist position: Be aware of your wrist position when engaging in activities that involve your wrists. Avoid excessive bending or twisting, and keep your wrists in a neutral position as much as possible.
It is important to consult with a qualified and experienced wrist surgeon to determine the most appropriate surgical option for your specific condition or injury. They can help explain the benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of each procedure, and work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan.

